Knee Bursitis
A structure looking like a sac is present in the knee joint which is filled with a fluid, called the bursa. They present where muscles meet the bone. Many bursae are present. Bursa reduces the friction at the time of joint movement. When the bursa becomes inflamed it is called bursitis. Bursa which is present on the kneecap is most commonly affected. Joint restriction is the commonest sign seen after bursitis.
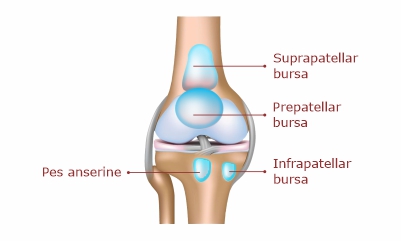
Types of Bursitis
- Supra patellar
- Pre patellar
- Infrapatellar
- Pes anserine
Causes
- Activities causing persistent movement of the knee joint
- Direct injury to the knee joint
- Infection to the bursa
- Complication after any disease like osteoarthritis, gout, or rheumatoid arthritis of the knee
Risk factors
- People who used to be in a kneeling position for a long time are more prone to have knee bursitis.
- Sports activities that put direct stress on the knee joint or any direct injury to the joint like while playing football, doing wrestling, etc. increases the chances of bursitis.
- Extra weight also puts over pressure on your knees, causing bursitis.
- Patients with osteoarthritis are also at a higher risk of having knee bursitis.
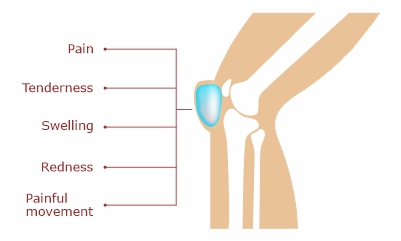
Symptoms
These depend on the affected bursa and the cause behind the inflammation. Common symptoms are:
- Pain in and around the knee joint
- Swelling around the knee joint
- Redness over the affected area
- Tenderness
- Painful knee movement
Prevention
How can you prevent knee bursitis?
- Wear kneecaps or knee pads to support and protect the knee joint.
- If you are in a standing position for a long time, start taking breaks in between.
- If you are used to doing squats on a regular basis try to reduce the time spent on performing squats.
- The ideal weight helps in releasing pressure on the knee joint.
Diagnosis
- Evaluate and compare both the knees, if one of the knees is found to be more painful.
- Examination of the knee joint to assess for any inflammation raised local temperature and for pain.
- Examination of the skin over the painful area for any reddening or signs suggestive of infection.
- Examination of the knee joints by moving the legs up and down to evaluate in which position the pain is more.
Investigations
- X-ray- Is prescribed to check for any bony injury or joint degeneration such as osteoarthritis.
- MRI- Bursa is visualized on MRI, so MRI is the best way to see the condition of the bursa.
- Ultrasound- This helps the doctor to visualize the affected area.
- Aspiration- Aspiration, and analysis of the fluid to check for any signs of infection.
Conservative management
- Over a period of time, bursitis has been shown to improve, so the aim of the treatment is relief in the symptoms. The treatment approach may depend on the cause and which bursa has been affected.
-
- Medications: To reduce pain and inflammation. Antibiotics are also prescribed in case of infection.
- Physiotherapy: Can help in reducing the symptoms, and also improves joint flexibility. A compression bandage will help in case you can not avoid the kneeling position and also help in reducing the swelling.
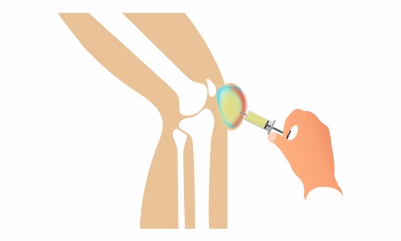
- Corticosteroids injection: If the basic medications are unable to contain the pain and improve the inflammation of the bursa, injection of corticosteroids may be administered into the affected bursa. This treatment has shown to reduce inflammation, but pain alleviation may take some time.
- Aspiration: The fluid from the swelling may be taken out, which will help reduce the size of the swelling and inflammation. Aspiration is carried out using a needle that is inserted into the affected bursa. After this procedure, a knee immobilizer may be advised for a short period of time. This knee immobilizer helps in reducing the chances of recurrence of swelling.
-
- Surgery
- As the last resort, if all the treatment modalities fail to improve the condition, the surgical excision of the bursa may be advised.
