Knee Effusion
In our joint, some amount of fluid is present naturally which works as lubrication and reduces friction to provide smooth movement.
When excessive fluid collects around the joint it is known as joint effusion. Effusion generally appeared as the swelling in the knee. The reason can be an injury, infection, or any medical condition.
Causes
- Ligament injury
- Bone fracture around the knee
- Gout
- Arthritis – Osteoarthritis/Rheumatoid arthritis
- Repetitive trauma or injury to the knee joint
- Any kind of infection in the knee joint
- Tumors or cysts
- Bursitis
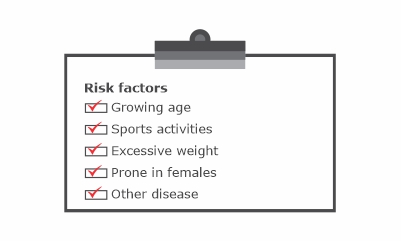
Risk factors:
Excessive stress on the knee joint and injury to the knee joint is a risk factor for knee effusion but there are other factors also that raise the risk of having knee effusion.
- Chances of knee effusion increase with age
- Sports activities include knee movement like basketball, wrestling, football, other sports that can twist or strain the knee joint.
- Excessive weight puts extra stress on your knee joint.
- Females, teenagers, and young adults are more prone.
- People who are suffering from osteoarthritis or any other joint disease are more prone to have knee effusion.
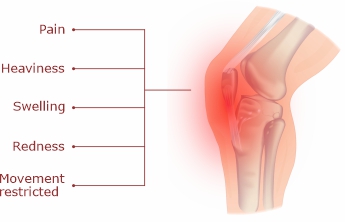
Symptoms:
- Can affect only one knee or both knees.
- Pain in the knee joint ( Pain increases on weight wearing), along with tenderness .
- Your feel heaviness in your knees.
- Swelling around the knee joint .
- Redness over the swelled knee .
- The joint becomes stiff due to swelling .
- Normal knee movement becomes restricted.
- The temperature of the affected knee is quite raised than normal .
- Your walking, Stair climbing, and day to day activities become difficult due to knee effusion.
Diagnosis
The patient comes with the complaint of a sore knee.
- The doctor will ask about the history of injury or any medical condition.
- Check the range of motion of your knee joint.
- Fluid aspiration from the knee to test – any infection, crystals, etc.
- X-Ray, MRI, Ultrasound, and CT scan can be prescribed to find the right cause.
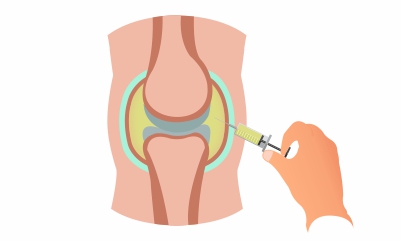
Treatment
Treatment depends on the cause of knee effusion.
- Pain killers and anti-inflammatory medicines.
- In case of infection- antibiotics are prescribed by the doctor.
- Corticosteroids- oral or through intra-articular injections.
- Arthroscopy treatment – to fix the damage.
- The joint fluid aspiration to reduce temporary pressure from the joint.
- Physiotherapy to enhance joint range of motion, to improve muscle strength, and flexibility.
- Self-Care
- Use knee support like knee braces or crap bandage ( as per your doctor).
- Give rest to the affected knee and avoid weight wearing from the affected knee.
- Do icing for 10-20 minutes to the affected knee, 2-3 times a day.
- Elevate your affected leg on a pillow above the heart level.
- Try to reduce weight.
- Do exercises regularly.
- Surgery
- If all these treatment measures fail, then surgery is needed to treat the cause of the effusion. In severe cases, joint replacement surgery is prescribed.
