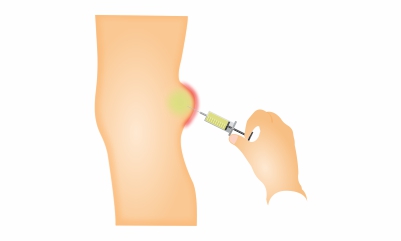
Popliteal Cyst/ Bakers Cyst
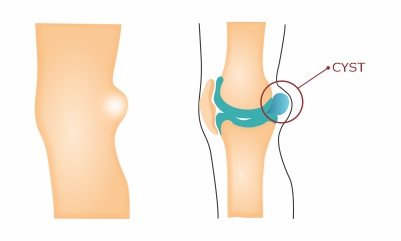
When the synovial fluid fills the sac-like structure, then a cyst is formed. When our knee joint produces an extra synovial fluid and when pressure increases in the joint, it pushes the fluid towards the backside of the knee and forms a cyst/bulge. This bulge is known as popliteal or baker’s cyst and it causes restriction of the movement and tightness of the knee joint. Pain increases in knee bending.
Generally, this happens due to any disease that affects the knee joint like cartilage damage or arthritis. By treating the underlying cause can reduce the problem. The popliteal (baker’s cyst) cyst usually does not have any long-term damage, but it is very uncomfortable, and chances of rupture are very rare.
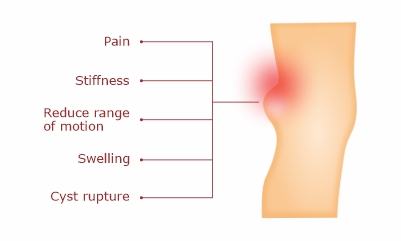
Symptoms
- Mild to severe pain
- Stiffness
- Compromised range of motion
- Bulge/swelling behind the knee and calf
- Discoloration around the knee and calf
- Cyst rupture
Diagnosis
- Physical examination
- Ultrasound
- X-ray: to check the bony injury
- MRI: Best investigation method to detect the soft tissue problem
Complications
- Severe pain
- Prolonged swelling
Treatment
Most of the time the cyst disappears on its own. But if not then you need proper treatment:
- Medication: The doctor may suggest corticosteroids to reduce the inflammation.
- Fluid drainage: Drainage of the fluid with a needle.
- Physiotherapy: Compression bandages and icing will help a lot in reducing pain and swelling. For the maintenance of muscle strength and a good range of movement of the knee joint, the physiotherapist may advise light exercises.
The doctor will try to treat the underlying cause of the cyst for example – if the cause is meniscus tear then there is a need for meniscus repair.